Goodwill is an intangible asset.
It is the reputation of the business.
That’s not an easily tradeable asset.
So, there is no readily available market for it.
We will understand the Concept of Goodwill with an example.

Example
Consider an entity, ABC Enterprises, which is into the manufacture and sale of Smartwatches. The number of new companies manufacturing and selling smartwatches is increasing day by day. So, ABC company came up with a new strategy.
It entered into a partnership with a well-reputed company like Apple (Very hypothetical example. But just for understanding) and promoted sales.
Financial Data:
The Manufacture cost of the smartwatch is $25
If it’s like a big player, consumers intend to buy at as high as $100 (4 times the cost).
That’s the power of brand value.
Said differently, the percentage of success would be insignificant even if the selling price is just above the cost (Say $30) for new players.
I hope the above example brought a good understanding of this Goodwill concept.
Lets move into the next topic
How and when do you recognize the Goodwill?
First, we will understand the types of Goodwill.
That will help redirect us to goodwill accounting as well.
What are the types of Goodwill?
- Purchased Goodwill
- Internal Goodwill
Purchased Goodwill is the Goodwill that’s recognized when a business is acquired at a higher price than its book value. For Example, Goodwill arises if a buyer pays $12,000 to purchase a company having a net asset book value of $10,000. The excess amount of $2,000 paid, is the Goodwill.
Internal Goodwill is self-generated Goodwill based on reputation or brand value. For example, an entity earns more than an average industry profit. That’s nothing but inherent brand value or Goodwill. There are various methods to calculate Goodwill, like Average Profits, Super Profits, and Capitalization.
We can learn more about those in a different article.
Goodwill Written off Journal Entry
Goodwill being an asset, will always have a debit balance. Every asset must be written off over its useful life.
The write-off is to match the revenue with expenses (Matching Concept).
For Intangible assets, we call this write-off as amortization.
The Journal entry for Goodwill write off is
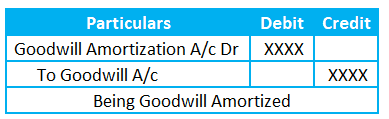
Runners Insight:
All Assets will have a useful life. This rule is not applicable to one asset. That’s Land.
Land is an asset that does not depreciate over a period of time. There will not be any wear and tear like a Plant & Machinery.
On Contrary, the value appreciates over time. So, we will not depreciate it.
Goodwill Written off Journal Entry FAQs:
When is Goodwill written off which account is credited?
Goodwill written off results in a reduction of goodwill assets. So, we will credit the goodwill account.
Is Goodwill written off an expense?
Yes, it’s similar to depreciation. We name it differently as amortization for the intangible assets. That’s because there is no wear and tear to deplete the value of assets. So, it’s a noncash expenditure.
What happens when Goodwill is written off?
Like any tangible fixed asset, Goodwill also has a limited life. We need to amortize it. The Value of Goodwill reduces to the extent of written-off.
How do you record Goodwill in a journal entry?
We record Goodwill as a part of purchasing any other business. Said differently, the purchase of a company includes acquisition of brand value.
For example, there is an established building with a restaurant known for its quality food. People associate that places not just with eating out but instead considers it as a restaurant that serves high-quality hygenic food and also consider it for good ambience. Business investors will opt to pay a higher price for that hotel than for other startups. So, this restaurant purchase includes the property (Tables, Chairs, Buildings, Interior work, etc.) but also the credibility of the restaurant. We call such fame/name Goodwill in accounting terminology.
Goodwill Journal entry is
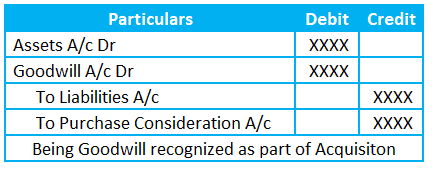
Note: Purchase consideration is the payable amount by the buyer to the seller as part of the business acquisition. As it is a liability for purchasing another business, we call it a Purchase consideration.
Let’s understand the above entry with an example.
Consider a business “Inferior Complex” with the following Assets and Liabilities.
- Assets = $10,000
- Liabilities = $6,000
- Capital =$4,000
So, the net asset value equals $4,000.
Who wants to sell an established business a break-even?
So, the seller demands an extra $2,000.
A Buyer, “Superior Complex,” wants to pay a higher price. This excess price over the net asset value is Goodwill.
Let’s record the entry for this example in the books of Superior Complex.
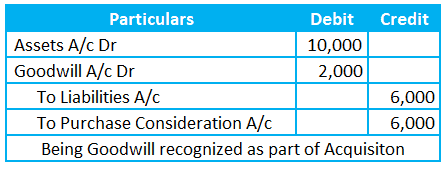
Note: Liabilities along with assets are transferred to the buyer from the seller in case of the Purchase/acquisition of a business.
Is Goodwill written off debit or credit?
Goodwill written off is an expenditure. We will debit the Amortization expense to record the Goodwill write-off and credit the goodwill asset account.
Goodwill Written off Journal Entry Summary
Goodwill is an intangible asset. We will recognize it with regard to purchase or acquisition of another business. Internal generated Goodwill is also another way of recognizing it. But that’s a low probable occurrence transaction when compared to the former one.
Like any other tangible asset, the intangible asset will also have an estimated useful life. We need to amortize it over the useful life. For example, a copyright, which has a limited life, is written off as per the Matching concept.
We will write off the Goodwill by debiting the amortization expense and crediting the Goodwill. Hope this article gave some solid understanding of amortization of goodwill.