Journal Entry is an accounting equation to record GL Accounts on debit and credit sides depending on the nature of the financial transactions. Golden Rules of Accounting forms the basis for deciding which GL account needs to be debited or credited. So, we will start with some basic things like accounting rules and then move on to journal entries questions and answers.

Table of contents
Golden Rules of Accounting
Golden rules of accounting form the basis for recording financial transactions. There are three category of accounts per these rules. The three categories of accounts – Personal, Real, and Nominal Accounts. So, the accounting rules that’s applicable depends on the category under which the GL accounts in the transaction falls into. So, we need to classify all GL accounts in the transaction under these category of accounts.
Personal Accounts
Personal accounts represent the persons. Those can be either Natural or artificial or representative personal accounts.
Natural Accounts: Transactions that involve individuals will comprises of Natural accounts. We do not see this often. But there can be GL descriptions with the names of the person.
Artificial Accounts – Companies, LLP, LLC, Partnership firms, etc.
Representative Accounts – Capital Accounts, Drawings, Prepaid expenses, Expenses Payable, etc.
Real Accounts
All the Assets fall into the Real Account. Examples will be Furniture, Computers, Cash/Bank, Property Plant and Equipment etc.
Recommended Article: Fictitious Assets (also called as Fake Assets)
Nominal Accounts
The word nominal means small. Accounts relating to income, expenses, losses, and gains fall under this category. We need to disclose nominal accounts in the statement of profit and loss. Here, Disclosure means transfer. Said differently, we will transfer those accounts to the Statement of profit and loss. Unlike Balance sheet accounts, these will not have a running balance from year to year.
Now we gained a good understanding of the three category of accounts. Let’s take a look at the Golden rules of accounting.

Modern rules of Accounting
Every study will have enhancements and accounting is not an exception. Therefore, the modern rules of accounting are also evolved. However, both the rules (Golden Rules or Modern Rules) result in same accounting journal entries.
The Major difference is the category of the accounts for which rules are applicable. Here, the accounts are of 4 categories like Asset, Liability, Income/Gains and Expenses/Losses.
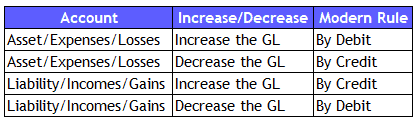
What are the steps involved in recording the journal entry?
1. Identify the GL Accounts within the Financial transactions
2. Determine the appropriate classification of these GL Accounts as per Golden rules of accounting or Modern rules of accounting
3. Apply the Applicable Accounting rule
4. Record the Journal entry
After recording the journal entry, ensure that the total of debits and credits is equal. Before we move into the accounting journal entries questions and answers, lets understand how to record entries with some examples.
Also Read: How to start journaling
How about some examples here to understand the Accounting journal entries?
JE Example 1
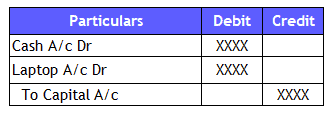
Ramesh started business with Cash worth $10,000 and Laptop worth $50,000. Record the accounting journal entries
Steps to record the accounting Journal entries:
1. Identify GL Accounts:
Cash GL and Laptop GL are the two accounts evident from the transaction. These two are assets, and there should be another account to balance the journal entry. It’s because the Assets are increasing and will stand on the debit side of the transaction. So, those assets are flowing into the business either by paying monetary value or Cash brought in by the business owner in the form of Capital. Therefore, Cash, Laptop and Capital Accounts are the GLs in this transaction.
2. Classification of GL Accounts:
Cash and Laptop are Real accounts (assets), and Capital is always a representative Personal Account (Liability) to the business. The Owner and Company are treated as separate and distinct as per the business entity accounting concept.
3. Golden Rules of Accounting: Assets are debited as they come into the business, and Capital will be credited as Ramesh is the giver.
Modern Rules of Accounting: The assets and Capital are increasing. We will debit the assets and Credit the Capital.
4. Record the journal entry
JE Example 2
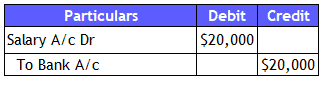
Backward Looking Company pays Salary of $20,000 to its employees
Record the Journal entry per Golden rules:
1. Salary and Bank Account are the two GL accounts in this transaction
2. Salary is a Nominal Account, and Bank is a Real Account.
3. We will debit the Salary as an expenditure under Nominal Account. The Funds are flowing out of business. So, Bank Account needs to be on the credit side.
4. Journal entry
Must read: Contra Entry and Goods distributed as Free sample Journal entry.
JE Example 3
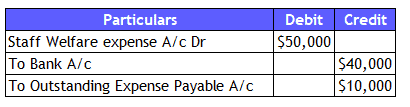
Loss Company is into the business of Trading of Cars. To Ensure its Employees are happy, they incur many staff welfare expenses like Food, Snacks, Team dinners/lunch etc. So, this month entity spent around $50,000 on staff welfare expenses. However, the entity paid only $40,000 due to the non-availability of Cash. The balance expenses are outstanding to ABC Bakery.
Record the Journal entry per Modern rules:
1. Identify the GL Accounts
The GL Accounts here are Staff Welfare and Bank Account. We need to prepare the accounts per accrual basis. So, we will record the Staff welfare expenses for the total amount relating to this current year. Per our understanding, there is some amount outstanding. So, there is a need to recognize a liability for $10,000. So, Outstanding expenses payable GL will also be part of this Journal entry.
2. Classification of GL Accounts
Staff Welfare is an Expenditure (Nominal Account), Bank is an Asset (Real Account), and Outstanding expenses payable is a Liability (Personal Account).
3.We need to debit the Expenses to increase them, credit the Bank Account to decrease it, and liability will be on the credit side to increase it.
4. Journal entry:
Also read: Income and expenditure account
JE Example 4:
Star Ink produces stationery items such as pens, pencils, A4 papers, and books. The company has been in operation for 20 years. The reach, however, is limited to national markets.
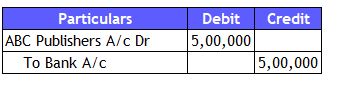
As a result, the company decided to expand its operations on a global scale. Therefore, plans to advertise with ABC Publishers were made, with a $500,000 investment.
Journal Entry to record the advertisement expense
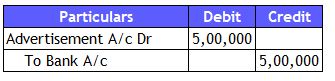
1) Cash Approach (Payment happens immediately)
Accounting Analysis:
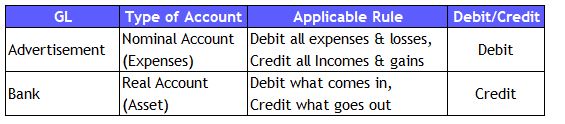
Journal Entry:
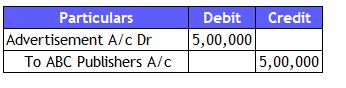
2) Credit Approach (Defers the payment)
Accounting Analysis
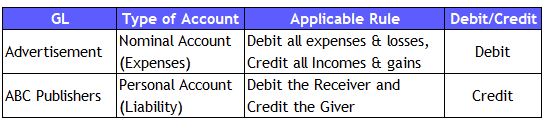
Accrual Entry
What’s the entry to record the payment?
Settlement Entry Analysis

Payment Entry
Types of Journal Entry
We got a good understanding of the concept of Journal entry, how to record it, and various steps and examples. Let’s move into understanding more about different types of Journal entries.
There are 8 different types of accounting journal entries as per their nature.
- Simple Entry
- Compound Entries
- Opening Entries
- Closing Entries
- Reversing entries
- Correction Entries
- Transfer Entries
- Adjustment Entries or Topsides
Simple Entry
Simple entry is a journal entry that involves only two GL accounts. So, one will be on debit side and the other GL on the credit side.
How about an example?
ABC Entity directors incur cab charges for attending a business meeting. This is an example of traveling expenses, and let’s see how to record them.

Old Newspaper Sale income is also a simple entry.
Compound Entry
The entry in which there will be more than two GL accounts is a Compound Journal entry. For example, there can be 1 debit GL and 2 credit GLs; 2 debit GL and 3 Credit GLs.
Let’s understand this with an example.
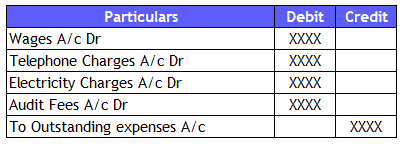
Simple company records the accrual of wages, telephone, electricity, and audit fee expense for the month, and these accruals are reversed on the first day of the following month.
Are you interested to purchase an accounting software. Check out tally and zoho accounting software
Opening Entries & Closing Entries
Any Business needs to move the net effect of all the Revenue, Expenses, Other Incomes, and Expenses (not relating to operations), Losses, or Profits, if any of the current accounting period, to Retained Earnings. As such, we need to close all the balances.
All these nominal account balances need not be carry forward to next year, and those balances reflect a specific period amount. The entry will be debiting the Net Profit or Loss and crediting the Retained Earnings. To Sum up, the closing entry is to transfer the result of operations to the capital account (Retained Earnings). These are Closing entries.
Runners Insight
The traditional method of accounting is through maintaining manual accounts. So, we need to carry forward all the assets and liabilities to the next accounting year. So, the entity is recorded similar to the below one.

Then, these GLs are brought down in the next year by debiting the assets and crediting the liabilities and capital accounts. Those are nothing but opening entries. But there is no such requirement due to the advancement in technologies. All the Accounting packages have the feature and will do the job with one click of a button.
Also Read: Cash Coverage Ratio
Reversing Entries
Journal entries are to account for financial transactions. Per Matching Accounting Concept, we need to record all the revenues and expenses relating to the accounting period. However, there is no guarantee that the accurate estimation of such items without invoices or the happening of the transaction. Therefore, entities record the best estimate of such amounts in the books as accruals at the end of the accounting period.
The accounting period is usually monthly. It can also be for a different period. As these are estimates and not actuals, we will reverse those transactions on the first day of the following period/month. Such entries which nullify the effect of the accruals are called Reversing Entries.
Runners Insight:
Don’t get confused these with the correcting entries. An example of Correcting entry is – if the entry is not correctly accounted for then we need to cancel it. Therefore, those correcting entries are different from these reversing entries.
How about an example to clarify this?
Fast Failure Company is into the business of Energy Producing company. So, entity invoices its customers for the current month on the first of the following month. But Fast Failure wants to ensure its accounts are appropriate before year-end, bypassing the accrual entry.
The Journal entry will be

The above entry is not reflecting the accurate amount. So, it will be reversed on the first of the following month and then recorded the entry based on the invoice. The reversing entry is

Correcting Entries
Journal entries which are accounted for fixing the errors in accounting the financial transactions. Here errors are like passing the JE with incorrect amounts or recording the entry to inappropriate GL accounts.
In Most Instances, these errors are not intentional or fraudulent nature. So, we need not consider those as window dressing of books. If there’s a perfectly plan and execution of such fraudulent entries, that’s not easy to find out.
Runners Insight:
Are you wondering how to handle such frauds ?
That’s why there will be audits performed to find all such issues. These audits can be Internal (by Management) or External (by Statutory requirements or Financial Institutions that fund the entity). So, these audits help in finding those frauds.
Let’s see an Example of Correcting journal entry.
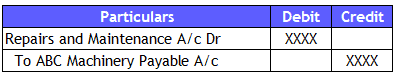
Slow Success company purchased a Machinery (fixed Asset) from ABC Machinery Company and incurred some expenditure for installation. As the accounting team does not have any experience in recording such transactions, they recorded it under Repair and Maintenance expenses (indirect expenditure).
Internal Audit team found the errors and suggested that such installation charges be capitalized as Assets.
Entry recorded by accounting team:
Suggestion from Internal Audit:
The already recorded Repairs account needs to be reversed, and the machinery account will be debited.

Runners Insight
All the expenses relating to the Asset need to be capitalized till it’s put to use. Refer to these articles to understand better Furniture, Machinery, and computers.
Transfer Entries
Transfer Journal entries are for recording the transfer of balance from one cost center to other. The other use is when expenses are spent centrally and then transferred to different units based on the agreed allocation methodology.
Also Read: True Up Journal Entry
Adjustment Entries
Adjustment Entries are the entries which are to record the accruals and deferrals. These entries ensure the following of matching accounting concept
Accruals are to record the expenses or incomes which relate to the current period (Cut off)
Deferrals relate the transaction where we need to
- Defer the recognition of Incomes till the revenue recognition criteria is me
- Defer the recording of Expenses over the period of benefit. These are nothing but deferred revenue expenditure
Accounting Journal Entries Questions and Answers
What is journal entry?
Journal entry is an accounting way of recording the business transactions. Each entry will have at least a debit and credit. Irrespective of number of GL accounts involved, there will be equal value of debits and credits.
What is journal entry example?
Lets consider the recording a direct expenditure – Carriage expenses. Here, Carriage is nothing but freight charges incurred for the purchase or sale of goods.
The two accounts here are Carriage Expenses GL and Bank GL. We need to debit the Carriage expenses because of its nature of being Nominal account and credit the bank GL as their is flow of funds outside the business. Therefore, the journal entry will be debiting the carriage expenses and crediting the business.
What are the 5 types of accounting journal entries?
There are different types of journal entries. We can group them as 5 broad types such as Opening & Closing Entries, Transfer Entries, Correcting entries and Adjustment entries. Refer to the above section for detail understanding of these.
Conclusion
Journal entries are to record all the business transactions so that it helps in finding out the results of operations and financial position. Such accounting journal entries follows Golden rules of accounting or Modern rules of accounting. These rules are framed based on different category of accounts like Personal, Nominal and Real for Golden rules, and Assets, Liabilities, Expenses/Losses, Incomes/Gains per Modern Rules. We need to account for the transaction on the basis of such classification and applicable rules for those categories.
There are different types of accounting journal entries like opening, closing, transfer entries, adjustment entries, correcting entries etc. Understanding these types of journal entries helps in identifying the entry to be used for recording the transactions.
