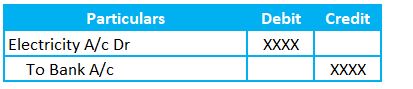
Record Paid Electricity Journal Entry by
- Debiting the electricity expenses
- Crediting the bank account.
What’s the purpose of Electricity JE?
To Records the power usage charges.
It can be direct or indirect expense.
How about an example here?
Consider an Entity.
Its into goods manufacture.
Assume it is a automatic process.
So, there is more demand for electricity.
Therefore, electricity is a direct expense.
When will be its a indirect expense?
In case of less direct dependence on power.
Table of contents
Paid Electricity Journal Entry
Why do we need to debit the electricity expenses?
Instead of debiting the electricity expense, can we credit the expenses?
For this, we need to understand the nature of the account and the group under which it falls for determining whether we need to debit or credit.
There are three broad categories of the accounts – Personal, Real and Nominal Account. So, we need to determine the Category of each GL in the transaction to apply the respective accounting rules.
This transaction involves two accounts – Electricity GL and Bank GL accounts.
The electricity account is an expenses account and falls under Nominal Account Category. Per Nominal Account Golden rules of accounting, debit all the expenses and losses, and credit all the incomes and gains. So, we need to debit the electricity account in the journal entry.
Bank Account is a Real account. Per Golden rules of accounting, debit what comes in and credit what goes out. So, we need to credit the bank account in the entry.
Runners Insight:
If you want to gain a good understanding of how to record the routine monthly expenses, refer to the topics – rent paid and telephone charges.
Alternative Treatment:
Accounting does not have any rules except the golden rules. So, there is a lot of flexibility regarding accounting a particular transaction . The alternative treatment for electricity journal entry is below.
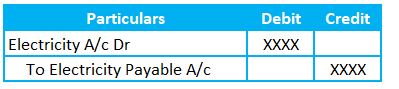
1) Accruing the Electricity Expenses
Electricity expenses and Electricity Payable are the two GLs here. We already have an understanding relating to the electricity expenses. So, let’s move on to the Electricity Payable. It’s a Liability account and relates to the Personal Account.
Per Golden rules of accounting, debit the receiver and credit the payer. So, we need to credit the Electricity payable account.
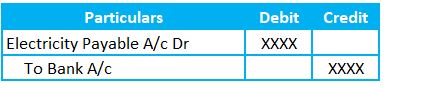
2) Paid Electricity Journal entry
Example
ABD is in the business of providing consulting professional services relating to taxation. So, it incurs an average monthly expense of $30,000 for electricity. ABD receives the electricity bills after the month-end. However, the entity needs to record the accrual of costs as part of the month-end reporting process.
Entry to record the accrual expenses
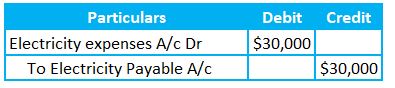
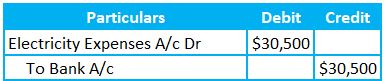
Later on, the entity received the electricity bill and noted that the current month’s charges are $30,500. So, there is a shortfall of $500 for the month. There are two approaches to recording these expenses.
1) Recording for the shortfall (or)
2) Reversing the accrual expenses on the first of next month and recording the actuals.
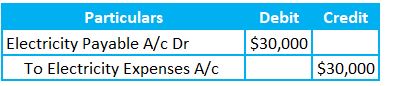
In General, entities adopt the second approach. So, the entity reverses the accrual entry and books for the actual expenses as below.
Reversal Entry
Actual expenses Entry
Summary of Paid Electricity journal entry
The paid Electricity journal entry is recorded by debiting the electricity expenses and crediting the bank account. These utility expenses are essential for any business to survive. The company will generally accrue these expenses at the end of each month and reverses the same on the first day of the following month. This step ensures that we consider all the period expenses as per the cut-off assertion. If there is any levy of taxes for electricity usage, then it is not required to have different GL head as the entity itself is its end consumer. We hope this article provides some clarity on the electricity journal entry.