What does Cheque Dishonoured Journal entry mean?
That means reversal of the following:
- Recorded receipt (Cheque receipt) or
- Payment transaction (Cheque Issue).
Let’s learn journal entries for each of the scenarios.
Cheque Dishonoured Journal Entry Scenario I:
The entity pays its vendor through a Cheque.
The Journal Entry (JE) will be debiting the vendor and crediting the Bank.
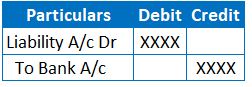
JE when payment of liability occurs through issue of a Cheque:
The below entry results in decrease of Liability and bank balance.
JE when the above Cheque results in dishonour:
If the Cheque issued by the entity gets dishonoured for insufficient funds, it increases back the liability and bank balance.
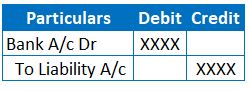
Because of dishonour entry, there is no reduction of liability or bank balance. So, this results in reversal of original entry.
Runners Insight:
A Cheque is a form of Bank payment. As such, Bank GL is part of the Journal entry due to any Cheque related transaction
Cheque Dishonoured Journal Entry Scenario II:
We learned the journal entry for issued Cheque dishonour in the above example. Let’s see the Journal entry for dishonoured Cheque, which is from debtors(Cheque receipt).
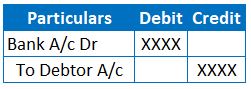
JE when the debtor pays back to the entity through a Cheque (Bank Balance increases and receivable balance decreases):
JE when the above Cheque receipt turns as dishonour:
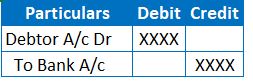
Cheque dishonour results in penalty charges by the banker to the account holder who issues the Cheque. Therefore, Cheque dishonour results in no change in Debtor balance and bank balances.
Also Read: NSF Check Entry
Examples:
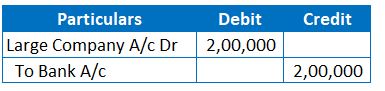
“ALL” company purchased raw materials worth Rs.200,000 from “Large” Company. Large Company pays by issuing a Cheque for the same amount. However, Banker dishonour‘s the Cheque due to insufficient balance.
What are the entries?
1. Entry for Purchase of Raw Materials
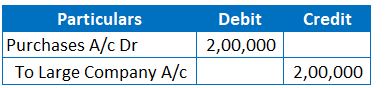
Here, a Large Company is a Creditor. As such, the Large Company will be credit in Journal entry to record the liability.
2. Journal Entry for Payment
3. Journal Entry for Dishonour of Cheque (Reversal of above JE 2)
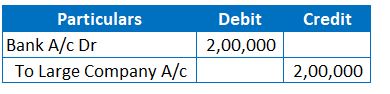
The above entry nullifies the effect of the second entry. So, there is no change in the liability or bank balances.
4. Journal entry for the penalty charges by the Bank
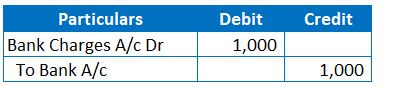
These are penalty charges by the Bank for the dishonour of Cheque’s. Refer to this article as example for charges levied by bank
Frequently Asked Questions:
How do I record a Dishonour of Cheque issued?
A Cheque dishonour results in recording a debit to Bank and credit to the liability.
Is dishonoured Cheque debit or credit?
If the Cheque received from debtors is dishonoured, then it results in recording the dishonour Cheque under the credit side of the journal entry.
If the Cheque issued to the Creditor is dishonoured, then the dishonoured Cheque is shown under the debit side of the journal entry.
Reasoning – Dishonouring of cheque results in no receipt of payment from the Bank. So, there is a reversal of bank GL to nullify the effect of an initial payment or receipt journal entry (Like 2nd JE in the above ALL Company example)
How is Dishonoured Cheque treated in a bank reconciliation statement?
Bank Reconciliation occurs to reconcile the bank balance per books to the bank balance recorded by the Bank.
Recording of the dishonour Cheque happens at the banks first. The entity records the reversal in their books on receiving the bank statements. So, there is a chance of dishonoured Cheque coming under reconciling items.
If Cheque is from debtors and gets dishonoured then reduce it from the Bank balance per book.
If the Cheque issued to Creditors gets dishonoured then Increase the Bank balance per book.
Generally, these Cheque dishonour does not occur frequently as it impacts the credibility and liquidity position of the business.
Do the reasons for Cheque dishonour relevant?
The answer would be not relevant for accounting purpose.
However, it is relevant for a business as a whole. Informing these kinds of transactions to the top management will be helpful for taking necessary actions.
Business Reason: It would show a negative impact on the business dealings. If the Cheque to the supplier (Payment) turns out as a dishonour, then the other party will have questions regarding the entity’s credibility and might not be willing in doing further business.
Conclusion for Cheque Dishonoured Journal Entry
Cheque dishonour means the bank does not allow the Cheque for payment or receipt. This results in non-payment if Cheque relates to supplier of goods or a non-receipt if Cheque relates to receivable. So, the resultant journal entry reverses the payment/receipt entry recorded.
The Journal entry for the Cheque dishonour is debit to the bank and credit to the liability, if transaction relates to Cheque payment to Suppliers (or) debit to the receivable and credit to the bank, if transaction relates to Cheque receipt is from debtors.
