Commission Receivable Journal Entry is to record the accrued Commission.
What does commission mean?
A commission is the payment made for completing a task.
For instance, marketing professionals are paid a commission based on the sales value.
What’s the purpose of employing commission approach?
The commission-based strategy is justified by the need to boost sales.
The commission-based remuneration for sales agents will be directly correlated with their effort.
Table of contents

Commission Receivable Journal Entry Example:
Quiet Company is a dealer whose business is to sell Air Conditioners of Noisy Company. Quiet company is an agent of Noisy company. The Commission rates are 5% on the value of goods sold and are paid once in 3 months (quarterly).
Quiet company current month sales are 100 ACs with total value of Rs.50,00,000. Commission receivable is 5% on Rs. 50,00,000, which equals to Rs.2,50,000.
So, Quiet company accrues the Commission receivable for the current month by debiting the receivable and crediting the income account for Rs.2,50,000.
Commission receivable is an income general ledger. The entity needs to check for the certainty of receiving the Commission before recognition those in the books of accounts.
Have you heard the term revenue recognition criteria?
Accounting of transaction requires adhering to certain rules, framework and standards set up by the governing bodies. So, the book keeping team shall follow their respective GAAP.
We have tried to add a couple of conditions below that need to be satisfied for revenue recognition.
- Transfer of ownership (Risks and Rewards) to the buyer
- Certainty in collection of receivables
- Measurability of sales amount
Note: The above conditions are not exhaustive. Its always best approach to check for the applicable GAAP and ensure to follow those appropriately.
How to record the Commission Receivable Journal Entry?
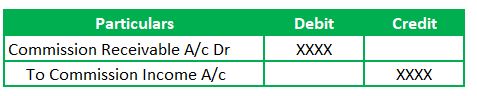
1. Commission Accrual Journal entry
Commission Accrual is also called as commission receivable account. Lets understand the nature of the GL accounts which are part of the transaction. Commission income Account is a nominal account, and Commission Receivable Account is a real account.
The next step is to identify the applicable accounting rules to record the journal entries. Rules are below:
- Real Accounts – Debit What Comes in and Credit what goes out
- Nominal Account – Debit all Expenses and Losses and Credit all Incomes and Gains
Recording the Commission accrual Entry:
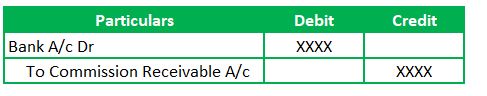
2. Commission Receipt Journal Entry
Commission receipt JE here is to record the proceeds received in the bank. Therefore, the relative GLs are Bank A/c (Real Account) and Commission Receivable A/c (Real Account). So, the Real Accounts – golden rules of accounting is applicable here.
Real Accounts – Debit What Comes in and Credit what goes out
Resources: Want to get more understanding of the debits and credits in the Journal entries? Read this article.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is commission receivable a debit or credit?
Commission receivable is an asset. So, we will debit the Commission receivable account to increase the asset balance with a corresponding credit to the commission income account.
Per the Golden accounting rules, we need to debit what comes in and credit what goes out. Commission will be receivable. Therefore, debiting the Commission receivable is appropriate.
Is Commission receivable an income or asset?
Commission receivable is an Asset GL as there will be inflow of funds. This Commission receivable GL is a parking account for a bank account. The bank account is hit when funds are received or paid.
There might be delay in receiving funds owing to the due date falling on a later date per terms and conditions of the commission contract. Even though this transaction does not involve cash receipts now, we need to ensure that accounting is done for this transaction. We can count this as similar to a credit sale.
Is Commission receivable an expense?
No. Commission receivable is asset account. As the Cash will be flowing into the business, it’s not expenditure.
Also Read: Rent Paid Journal Entry
How do you record brokerage fees in accounting?
Brokerage fees can be either income or expenses, depending on the nature of transactions. Let’s take a classic example relating to stock purchase. Mr. Lazy opens a Demat account with the Loss holder stock broking company. Mr. Lazy buys ten shares of ABC Company by paying 0.5% brokerage to the Loss Holder share broker.
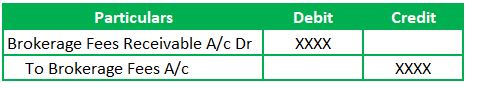
Journal entries in the books of Loss Holder Share broker,
Brokerage fees are the income. Those fees are payments against facilitating its customer to purchase and sell shares.
Conclusion:
Commission Receivable Journal entry is to record asset and income. Said differently, this is to record on the basis of accrual accounting. There will be deferment of receipt. But we need to record the transaction as it occurs. So, Commission Receivable being a real account will be debit and Commission Income shall be on the credit side of the Journal Entry.
