The name itself indicates that this travelling expense relates to expenses incurred for travel by entity employees or directors. The purpose of travel shall be connecting to the entity’s business operations. Therefore, the purpose shall not be of personal nature.
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes

Travelling expenses Examples:
Let’s see a couple of instances relating to travelling expenses
- Directors Cost of travel to other City to attend some business meeting or Client meeting
- Cab Expenses (Local Travel)
- Air Fare and insurance charges, if any relating to the business travel
- Expenses incurred for the Meals, Communication charges and WIFI Charges
- Tips or Surcharge paid for using any of the above facilities as part of travel
- Parking Fees, Toll Charges, Cab Waiting Charges and Luggage Porter Charges
What’s the Journal Entry?
Travelling expenses is a Nominal Account that flows into the Profit and Loss A/c. As this GL is an expenditure Account, the appropriate accounting treatment is to debit this GL Account in the Journal Entry.
Let’s see what’s the corresponding Credit.
Credit is for the Liability Account. Here Liability Account is named Cab Charges Payable, Travel Charges Payable etc., based on the nature of the liability.
There might be instances where there is no requirement to recognize the liability like Meals, tips, parking fees etc. These expenditures are paid immediately, and there might not be any bills or invoices. So, the Credit, in this case, is the Cash A/c.
Journal Entry for recording the Travelling expenses:
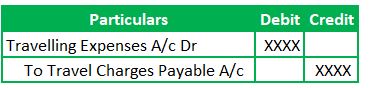
(Being the travel charges incurred for ABC Manufacturing deal)

(Being the travel charges paid)
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Are the Travelling expenses of a Salesman forms part of Direct or Indirect Expenses?
The category of expenses depends on the nature of the entity’s business.
For Entities exclusively into the Marketing/Product Sales (not manufacturing), the Travel expense of a Salesman is a direct expense. That’s because those expenditures drive the business operations of the entity.
For Entities not falling into the above category, those travel expenses fall into the Marketing Expenses category, which is an indirect expense. Therefore, it depends on the business category in which the entity operates.
2) What does Accommodation expenses mean?
Accommodation Expenses are the expenses relating to hotel or motel stay. These expenses include the Food, Laundry Service, Telephone, Internet expenses, GST and Service Charges. So, these Accommodation expenses are part of travel expenses. Therefore, it qualifies for indirect business expenditure.
The thumb rule here is to check whether the accommodation expenses shall be relatable to the business operations. So, emphasis shall be given to business importance of the expenses.
3) Paid for travelling expenses journal entry:
Paid for Travelling expenses journal entry records the cash/bank payment done for the travel and related expenses incurred for the business purpose. Let’s see the nature of accounts and accounting rules applicable.
Accounts Involved – Travelling expense and Bank Account
Nature of Accounts –
Travelling Expenses is a Nominal A/c – Expenditure and Bank Account is Real A/c – Asset
Accounting Rules:
The Golden rules of accounting applicable in this scenario are below.
Nominal Account: Debit the expenses and Losses Credit the gains and incomes and
Real Account – Debit what comes in and Credit what goes out
Paid for travelling expenses journal entry is
Travelling expenses A/c Dr
To Bank A/c
4) Travelling expenses are debited to which GL account?
There are no rules for the Naming of an Account. The GL Description shall depict the nature of the Account. For example, if the GL relates to telephone expenses, it shall not fall into conveyance expenses. Therefore, the travelling expenses GL is used as a debit to record the travel expenses in general.
Conclusion:
Travelling expenses are the expenses incurred in relation to business travel. The purpose shall not be in a personal nature. The thumb rules are to check if those expenses help further business operations. This travel expenses category is wide enough to cover the accommodation charges, telephone, internet charges, ancillary charges incurred along with the hotel expenditure.
Debit the Travelling expense and Credit the Bank Account to record the Journal Entry. If the transaction happens on a credit basis, two entries are recorded. The first one is to debit the travelling expense, and the Credit is to the Liability Account. The second entry is to debit the Liability account and Credit the bank account. The net effect is knocking off the Liability Credit in the first entry and the Liability debit in the second. So, technically the journal entry is the same as the first scenario. It’s just deferment of recording the complete transaction effect.
Hope this article brings some clarity on the travelling expenses concept. If you have any questions then pls let us know through the comments below.