
Bank Charges Journal Entry does not have any unusual accounting treatment. So, its similar to any other expenditure journal entry. Bank Charges are expenses to the account holder and income to the Bank.
Table of contents
What’s the Bank Charges Journal Entry?
In the Books of Account Holder,
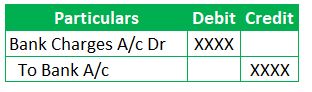
(All the Fees or Charges by Bank to its Account Holders are debited to one GL – Bank Charges A/c. However, it’s not a hard and fast rule that all bank charges need to be recorded in only one GL. So, Entities can record this kind of transaction in multiple GLs such as Cash Handling Charges GL, Overdraft Fees GL etc. The primary reason for recording at multiple GLs is to track the expenses separately.)
Read also: Concurrent Audit of Banks Guide
Understanding the Bank Charges Journal Entry in the books of Account Holder
Cash Handling Charges:
Banks allow certain limits for deposits or withdrawal cash. So, there are no charges if the transactions are within the said limit. For example, Bank mandates for charges if the cash deposited in the current account exceeds Rs.1,00,000 per day. Cash handling charges are Rs.1 per each Rs.1,000 deposit amount on the same day.
Each bank has a different policy for the service charges. So, Cash handling charges are the charges levied by bank for providing cash deposit services to the account holder.
Why are Cash handling charges levied?
All these increased charges are to encourage online transactions as part of digital transformation growth.
When are these Cash handling Charges levied?
These charges are levied as and when the transaction happens. So, the bank deduct the cash handling charges from the deposit amount and deposits the balance into the customer account.
Runners Insight: Cash handling charges are triggered as and when the limits are exceeded and the fees are deducted on total of all transaction.
Example:
Wanna see an example that triggers cash handling charges?
Lets take reference of bank charges policy from the above example. Assume XYZ is account holder of ABC Bank.
- Scenario I – The total of deposits is Rs.99,800 on the day. No Charges are levied
- Scenario II -The total of deposits is Rs.100,100 on the day. Charges are levied as and when the limit is triggered.
Assume the total of deposits is Rs100,100 on the day and 11 deposit transactions happened on that day for this XYZ account holder.
The value of 10 deposit transaction is Rs.99,800. The last transaction value is Rs.300. So, charges are not levied till 10 transactions. Fees are deducted after occurrence of the 11th transaction.
Charges are levied on all transactions not just on the 11th transaction which triggered the limit.
Total charges = 100,100*1/1000 = Rs.100.10
In the Books of Bank,
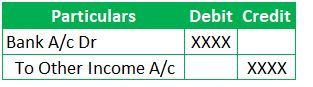
(Here, Bank Account debited represents the Cash inflow to the Banks for Other Income. Here Other income means the non primary source of income such as Savings Account Maintenance Fees. Banks majority income comes from the interest earned on various types of Loans sanctioned such as Personal Loans, Home loans, Gold Loans, Agriculture Loans, Overdraft, Cash Credit etc.)
Understanding the Bank Charges Journal Entry in the books of Bank
Now that we learned about the accounting treatment of bank charges, we will move on to understand some basics such as what are bank charges, why are they levied etc.
Bank Charges
Bank Charges are the transactional fees for the various services provided by bank . It does not include the interest charged on the loans.
What are Bank Charges?
Service Charges levied by Banks for transactions such as Maintenance Fees (E.g., Debit and Credit Card Annual Fees), Transaction Fees (E.g., Cash Handling Charges), Fees for Issuing bank statements etc. The List is never-ending. Find example of bank charges here.
Why are the Bank Charges Levied?
Any business can sustain itself based on profits and income in the long run. A major source of income for banks after Interest income is the transaction charges.
All the facilities used by the account holders at Bank require payment of bank charges or fees.
Note: Banks are also required to charge the GST on the total value of bank charges levied. So, account holder tend to record the bank fees along with all taxes levied.
Runners Insight: The interesting fact for this expense is that there will not be any liability account in this JE. This is because most often the fact that charges are payable is known after the happening of transaction. Account holders get this information from Bank statements.
Conclusion for Bank charges Journal Entry:
Bank Charges Journal entry is similar to an expenses JE. We record this entry by debiting the Bank charges GL and Crediting the Bank GL.
