We can infer from the Article name, “Outstanding Expenses Journal Entry” that the journal entry relates to the expenses which are not paid but incurred.
Confused?
Let’s break it down.
Business thrives based on credit allowed by its suppliers and permitted credit to its customer. So, the entity incurs expenditure without the actual requirement of clearing the payment at the exact moment. There is a credit period for clearing dues.
Therefore, business can settle the expenditures within that credit period. So, the word outstanding implies that an expenditure is incurred and payment is due.

Table of contents
How about an example here?
Facts of the Scenario
Loss Company is into the restaurant business. The major expenses are staff salary, rent, electricity, maintenance charges, cost of vegetables, fruits and groceries.
The company policy is to pay the staff salary, Maintenance and grocery bills (all outstanding expenses) on 5th of next month. The current month is May.
May month expenditure which will be payable in June is $10 Million and April month expense paid in the May month is $9 Million
Restaurant needs to present their monthly final accounts (Balance sheet, Profit & loss, cash flow statements) to their board of directors. So, it is closing the books of accounts.
The Problem
As the May month expenses are not paid in the same month, accountant thinks that the current (May) month expenses will be $9Million.
Does this approach sounds good?
Nope. Its against the matching concept of presenting the current period expenses along with income.
Even though there is a delay in payment, the expenses or income that needs to be accounted shall be as per actuals current period data. So, the current expenses in the above example shall be $10 million.
Outstanding Expenses Journal Entry

Understanding Outstanding Expenses Journal Entry
When it comes to recording the Outstanding expenses entry in the Journal, there are a few different steps involved. Those steps include identifying the GL accounts, finding out which accounting rules apply to them, and implementing them. Let’s get right down to cover each and every one of these processes.
What are the GL Accounts involved in this transaction?
Two GL accounts which are part of this transaction are – Expenses GL and Outstanding Expenses GL.
What are the applicable rules?
Every field has its own canon of guiding rules and principles. There is no exemption to accounting.
We must adhere to those fundamental principles of accounting. Let’s look at the regulations that apply to each GL and see what they are.
Outstanding expense GL being a liability account falls into the category of Personal account. The other one is an expense GL and it relates to Nominal Account Category.
Do you remember the 1st and 3rd Golden rule of accounting?
First Rule
It’s relating to the personal and liability accounts, which says that – “Debit the Receiver and Credit the giver.”
Third Rule
It’s relating to the Nominal accounts, which says that – “Debit all Expenses and Losses and Credit all Incomes and Gains”
From above, we can infer that this rule comes into play at Profit and Loss statement.
Accounting equation
Debit Side: Debit all Expenses for the total amount because it’s a nominal account.
Credit Side: Business incurs expenditure and is due. So, there is a requirement to give from the entity which incurs it. Therefore, the liability account will be on the credit side.
Practical Example to understand the Outstanding Expenses Calculation:
We have understood the accounting concept. But, arriving at best estimate of outstanding expenses is challenging especially if it involves variable expenses. This because variable expenses will not have any standard or base to estimate.
For example, a entity provides facility to its employees for claiming reimbursement of commuting expenses. Its not possible for accurate estimate as there is no standard base. These will not be known until the actual expenses are incurred.
How about an example for understanding how the estimation process works?
Example 1
A Ltd company is a second-hand Car dealer and is also known for its multi-brand car repair services. The Company’s significant expenditure for repair services is salaries to the automobile mechanics, electricity, and water charges.
The Company clears the expenses once every three months. It helps in ensuring adequate working capital flow for the business. The details of expenses are:
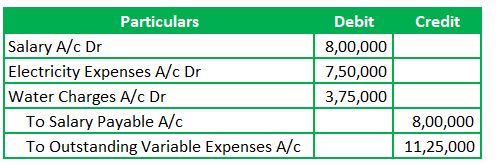
- Fixed Salaries – $800,000
- Variable expenses – These are based on the service repairs performed each month. The Company records the variable expenses for each month as outstanding. Settlement happens every quarter.
Number of car service repairs performed – 15,000
Based on historical data, Company determined an average estimate of all the variable expenses per Car Service –
- Electricity – $50
- Water Charges – $25
Total Variable Expenses – 15,000*75 = $11,25,000
This is how expenses are estimated and recorded as accrual in books of accounts.
Journal Entry
Let’s see the outstanding expenses journal entry-
Runners Insight
In General, Car service Centre will not show a break up for electricity and water charges. Instead, they charge a blanket amount from the customer. However, companies adopt different methods to estimate accurately based on their experience and industry data.
The above illustration to help readers understand how the companies estimate expenditure. In other words, there isn’t any formula for the method of estimate. So, it varies based on the expenses which are being estimated.
Example 2
For instance, if the company policy states that it reimburses all commuting expenses between the office and employee home.
Will there be any probable estimate?
The answer would be no. It’s not possible.
Employees might choose different options – Two-Wheeler services, Cabs, Public transport, etc.
The best way is to take the previous year’s actuals and add some percentage for inflation.
How about if that’s the first year of implementing the reimbursements?
The Company will list down the total employee’s number and consider 20 Km as the average distance between office and home. Then, arrive the total estimated costs as below:
Estimate = Number of Employees * Cab Charges for 20 KM * 2
Companies might add some 15% percentage to this considering the peak charges levied by Cabs. Thus, expenses estimation is driven by many factors.
Benefits of Recording Outstanding expense Journal Entry
- Recording outstanding expense journal entry brings several benefits to any business organization. The details are below
- Tracking all the outstanding expenses accurately and recording those promptly in the appropriate ledger allows businesses to maintain accurate records of payments due and outstanding balances.
- Accounting of these expenses can help identify late outstanding payments more quickly, which can help improve cash flow. The quick cash inflow into the business reduces the working capital requirement, lowering interest costs.
- Proper Recording of outstanding expenses helps to have a checkpoint on the related items such as interest on overdue payments, bank charges, etc., enabling companies to keep their finances organized.
- Investing in a Sound outstanding expenses journal entry system (refer below) is essential for safeguarding effective bookkeeping for any business.
- Additionally, we can monitor outstanding expenses over time to identify if certain expenses are becoming more frequent
Thus, using an outstanding expense journal entry benefits the company’s financial health.
What do you mean by a Sound outstanding expenses journal entry system?
- Understand the type (E.g., Yearly, Half yearly, or Monthly) and nature (E.g., Insurance expenses, Power consumption) of accounting entries that need to be recorded.
- Start keeping a running list of all transactions. This list should contain all transaction details such as amount, date, Invoice/PO number, and vendor details. Excel Spreadsheet is a great tool for these kinds of Jobs.
- Accounting software can reduce your manual job to some extent. We can generate a list of transactions from it as well. It might not give you an exclusive list, as new transactions occur in the current period. But it can serve as a good starting point for keeping those lists.
- Generally, business records all the Outstanding expenses on a day near the end of the month. So, ensure all the expenses in the list are posted on the last Friday/Working day of the month.
- A proper review of those entries shall be part of the process. The reviewer should be independent of the preparer.
- Have a Checkpoint as well. These expenses are routine. So, the total of all current month/period outstanding expenses posted shall equal or near the amount of the prior month’s expense.
Conclusion
Outstanding Expenses is an expense incurred but not paid. The Journal entry will be a debit to the expenses and credit to the liability. It’s best to name the expenses and liability accounts with a more identifiable description/name.
Outstanding Expenses Journal Entry

What’s the Journal entry for recording payment of expenses?

So, the net effect is a debit to the expense GL and Credit to the bank GL as the outstanding expenses account nullifies.
Recommended Articles
Best way to learn the Journal entry is to memorize the three golden rules of accounting and practice as much as possible different Journal entries. So, we have a list of different entries below for better understanding:
