Accrued Audit fees Journal entry relates the audit fees which is incurred but not paid. Hence it relates to outstanding expenses.
So, that’s a liability account.
Audit fees are expenses charged by the audit professional against verifying and testing the books of accounts of business.
Such auditors can be internal or external.
Internal auditors are appointed by management to ensure the established system, procedures and controls are functioning as anticipated.
The Reports of these findings are not made public. However, the external auditors are to audit the books and will opine whether the financial statements represent a true and fair view. Therefore, such audit fees paid to both the internal or external auditors are expenditure to the business. Such audit fees journal entry will be similar to any other expenses entry of the business.

Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
What does word “incur” means here?
Every financial transaction will have two aspects. Said differently, there will be some inflow of benefit against an outflow of benefit.
Example 1:
Lets assume you buy a pen worth Rs.10 from a book shop. The benefit coming in is a pen worth Rs.10, and the benefit you are losing is the equivalent money.
Before understanding the term ‘ incur ‘, let’s move into a higher-level example.
Example 2:
Companies appoint an auditor to verify the books of accounts and issue an opinion on those. Let’s see the benefits here –
Benefits Received – Audit Service
Benefits Given – Money
Let’s Learn the definition of the term “Incurred”
Definition for the term Incurred:
Incurred is a term used in case of where the benefits are received but the amount isn’t paid for that. So, the second aspect of the transaction (Payment) is yet to complete here.
Accrued Audit Fees Journal Entry:
The two General Ledger (GL) accounts in this transaction are accrued audit fees A/c and audit fees A/c.
Let’s see what are the debit account and credit accounts here.
1. Audit Fees GL is an Expenses account. Per Nominal Accounts Golden Rule of Accounting, Debit all Expenses & Losses , and Credit all Incomes & Gains.
2. Accrued Audit Fees GL is the Personal Account. Per Personal Account rule, Debit the receiver and Credit the giver.
JE 1 – Journal Entry when Accrued audit fees are incurred:
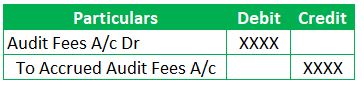
The audit fees is payable and due to auditor. So, we need to credit the liability account. Often, book keepers tend to ensure that the GL name to include the details of to whom the liability is due.
Lets say, the Liability is due to M/s. ABC & Co. Then, the liability GL will be ABC Accrued Audit Fees. This approach of naming the GL accounts is more convenient.
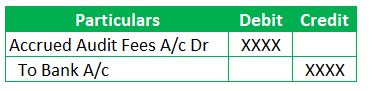
JE 2 – Journal entry when the expenses are paid:
JE 3 – What is net entry for Accrued Audit Fees?
Accrued Audit Fees GL gets nullified. The net entry is
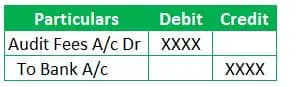
Generally, the above third entry comes into picture if there is no delay between incurring the services and the payment date. If there is no credit period, then there is no requirement to affect the Accrued audit fees GL in the Journal Entries.
However, it’s common to follow the above two entries instead of just the net entry, even in case of no credit involved.
Practical Challenges for recording Accrued Audit Fees Journal Entry:
Accrual of Audit fees happens if the entity does not receive the invoice before the closing of account books (Year-end).
Sometimes, the audit fees also involve the out-of-pocket expenses incurred by the auditor and his team. Out of Pocket expenses include travel expenses, accommodation charges, conveyance charges, and food expenses.
The best estimate is considering the previous year’s audit fees and adding any nominal increase (Say 5%). The other important point to consider here is to check the audit scope for the current year.
How about an example here?
Let’s say Stock Audit Fees are the subject of this Journal entry. Historically, the entity requests auditors to perform the stock audit of all its Go-downs. However, the entity started a new branch to expand its business to other areas in the Current Year. The entity wants to get this branch also under audit purview.
This scenario is a clear-cut situation of increased work and scope. So, there will be an increase in the audit fees. So, the entity needs to increase the audit fees considering this as well.
In General, Auditor and management discuss this fee before the commencement of audit work. The accounting team shall coordinate with the management to get a proper audit fee estimate.
Conclusion:
Accrued Audit fees journal entry is an entry to record the accrual of audit fees for the year. The general question for recording any of these entries is – Why shall we record the audit fees journal entry even though the payment does not happen. This accounting treatment is to adhere to the accrual basis of accounting. Accrual basis means recording the transaction irrespective of receipt or payment of cash, at the same time or at a later point in time. The Journal entry is debit the Audit Fees GL and credit the Accrued Audit Fees or Bank if the amount is paid immediately.
